AXILLARY CRUTCH, child, adjustable height, 90-120 cm
STD
EPHYCRUA2C-
Valid Article
HS Code:
903300
Last Updated on:
29/06/2025, 23:44:44
Former
Code(s):
EPHYZFR0030
Y12030603 - Crutches with under-axle support
European Medical Device Nomenclature (EMDN) is the nomenclature of use by manufacturers when registering their medical devices in the EUDAMED database. EMDN is characterised by its alphanumeric structure that is established in a seven-level hierarchical tree.
AXILLARY CRUTCH
Definition
A staff-like mobility aid used to assist a person with a disability to support their weight while walking.
The device has one leg, a padded hand support at the level of the user's wrist, and an under-arm (the armpit or axilla) padded platform.
Synonym
Specifications
Quality standards
ISO 24415-2, 2011, edition 1, (confirmed 2022) Tips for assistive products for walking - Requirements and test methods - Part 2: Durability of tips for crutches
Technical specifications
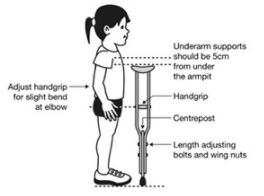
- Identification of the size needed: measure the length between two following points:
- 5 cm below the axilla to
- the 5 cm anterior and 15 cm lateral to the foot in standing position
- Height adjustable with butterfly screws
- Made of aluminium
- Rubber tips with metal inlay (for longer resistance)
- If possible with ergonomic hand grip
- Hand grip height adjustable (average sizes):
| Age group | size | of patient | of crutch |
| Child/adolescent | small | 130 - 150 cm | 90 - 120 cm |
| Adult | medium | 150 - 175 cm | 110 - 140 cm |
| Large adult | large | 175 - 198 cm | 130 - 150 cm |
- Dense foam for hand grip and underarm support
- Supplied per pair
Instructions for use
For people unable to put weight on a lower limb (elderly people, amputees …).
Take the morphology of the local population into account when thinking about the size of crutches to be ordered.
Check if the patient received adequate training for the use of axillary crutches, and also for the detection of any sign of compression of the axillary neurovascular bundle.
MSF requirements
Mobility aid used in all types of contexts.
Some restricted information has been hidden. Sign in
to see this information